This post will show how to perform typical CRUD (create, read, update and delete) operations in AngularJS when consuming a RESTful web service.
A prerequisite for this demo is a working RESTful web service. For a basic introduction on creating a Java based RESTful web service, see my introduction on how to consume a RESTful web service with AngularJS created by a Java backend. For completeness sake I’ve added a Java based sample at the end of this post.
Frontend (AngularJS)
Views (Partials)
We will create three views.
The first view will display all users (user-list.html):
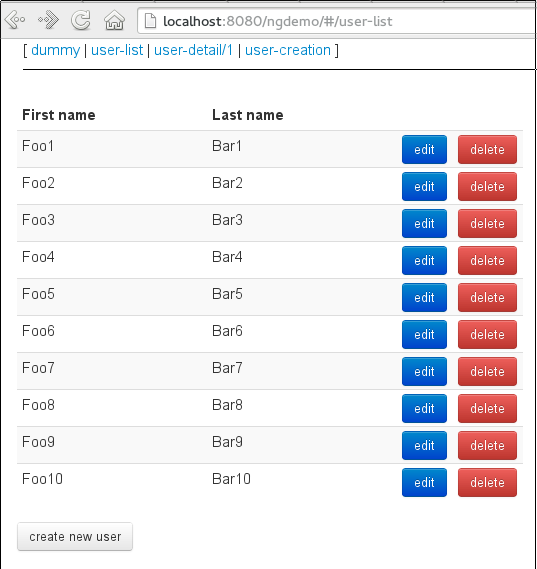
The view also provides links to edit (ng-click="editUser(user.id)") and delete (ng-click="deleteUser(user.id)") specific users as well as a link to create a new user (ng-click="createUser()").
{% codeblock %} {% raw %}
The second and third view (user-detail.html and user-creation.html) both provide a form for entering the user properties.
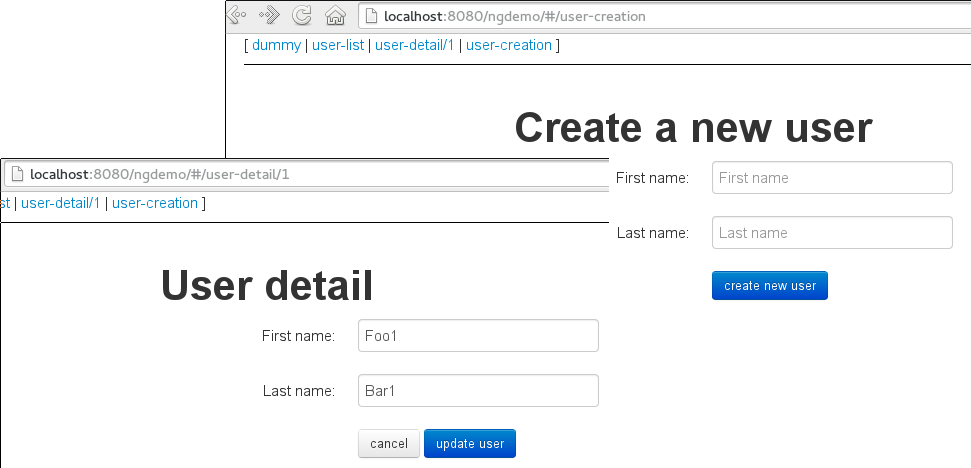
They only differ in the actions provided. These actions (cancel(), updateUser(), createNewUser()) are invoked using ng-click:
<div class="container">
<h1>User detail</h1>
<form novalidate="novalidate" class="form-horizontal">
<div class="control-group">
<label class="control-label" for="inputFirstName">First name:</label>
<div class="controls">
<input type="text" id="inputFirstName" ng-model="user.firstName"/>
</div>
</div>
<div class="control-group">
<label class="control-label" for="inputLastName">Last name:</label>
<div class="controls">
<input type="text" id="inputLastName" ng-model="user.lastName"/>
</div>
</div>
<div class="control-group">
<div class="controls">
<!-- user-detail.html: -->
<a ng-click="cancel()" class="btn btn-small">cancel</a>
<a ng-click="updateUser()" class="btn btn-small btn-primary">update user</a>
<!-- user-creation.html: -->
<a ng-click="createNewUser()" class="btn btn-small btn-primary">create new user</a>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
Controller
Next we will create three controllers corresponding to the three views.
UserListCtrl
UserListCtrl provides three functions editUser, deleteUser and createUser.
editUserandcreateUsermerely redirect to a different partial view using AngularJs’s$locationfunction.deleteUsercalls theUserFactoryservice methoddelete(which we will create shortly).
Furthermore the $scope.users is filled with the result from the UsersFactory.query() function.
Note that all required dependencies are injected into the controller’s signature (function ($scope, UsersFactory, UserFactory, $location)).
var app = angular.module('ngdemo.controllers', []);
app.controller('UserListCtrl', ['$scope', 'UsersFactory', 'UserFactory', '$location',
function ($scope, UsersFactory, UserFactory, $location) {
// callback for ng-click 'editUser':
$scope.editUser = function (userId) {
$location.path('/user-detail/' + userId);
};
// callback for ng-click 'deleteUser':
$scope.deleteUser = function (userId) {
UserFactory.delete({ id: userId });
$scope.users = UsersFactory.query();
};
// callback for ng-click 'createUser':
$scope.createNewUser = function () {
$location.path('/user-creation');
};
$scope.users = UsersFactory.query();
}]);
/* ... */
UserDetailCtrl and UserCreationCtrl
UserDetailCtrl provides the function updateUser, which in turn invokes the service method UserFactory.update. The $scope.user is filled with the result from calling UserFactory.show. cancel is just a convenient link redirecting back to the user-list view.
UserCreationCtrl provides the function createNewUser, calling UsersFactory.create.
Again, both controllers use $location to redirect back to the user-list partial view.
/* ... */
app.controller('UserDetailCtrl', ['$scope', '$routeParams', 'UserFactory', '$location',
function ($scope, $routeParams, UserFactory, $location) {
// callback for ng-click 'updateUser':
$scope.updateUser = function () {
UserFactory.update($scope.user);
$location.path('/user-list');
};
// callback for ng-click 'cancel':
$scope.cancel = function () {
$location.path('/user-list');
};
$scope.user = UserFactory.show({id: $routeParams.id});
}]);
app.controller('UserCreationCtrl', ['$scope', 'UsersFactory', '$location',
function ($scope, UsersFactory, $location) {
// callback for ng-click 'createNewUser':
$scope.createNewUser = function () {
UsersFactory.create($scope.user);
$location.path('/user-list');
}
}]);
Don’t forget to map the views to the corresponding controllers in app.js using the $routeProvider:
angular.module('ngdemo', ['ngdemo.filters', 'ngdemo.services', 'ngdemo.directives', 'ngdemo.controllers']).
config(['$routeProvider', function ($routeProvider) {
$routeProvider.when('/user-list', {templateUrl: 'partials/user-list.html', controller: 'UserListCtrl'});
$routeProvider.when('/user-detail/:id', {templateUrl: 'partials/user-detail.html', controller: 'UserDetailCtrl'});
$routeProvider.when('/user-creation', {templateUrl: 'partials/user-creation.html', controller: 'UserCreationCtrl'});
$routeProvider.otherwise({redirectTo: '/user-list'});
}]);
Service
AngularJS can consume the web service using $resource. This module is injected via 'ngResource'.
We create two factories:
UsersFactory(note the plural s) calls the web service with methods not requiring an id (queryandcreate).UserFactorycalls the web service with methods requiring a user id (show,updateanddelete).
var services = angular.module('ngdemo.services', ['ngResource']);
services.factory('UsersFactory', function ($resource) {
return $resource('/ngdemo/web/users', {}, {
query: { method: 'GET', isArray: true },
create: { method: 'POST' }
})
});
services.factory('UserFactory', function ($resource) {
return $resource('/ngdemo/web/users/:id', {}, {
show: { method: 'GET' },
date: T
slug: "restful-crud-with-angularjs"
aliases: [/blog//restful-crud-with-angularjs]
delete: { method: 'DELETE', params: {id: '@id'} }
})
});
Backend (Java)
Here is an example of a RESTful web service created with Java:
package ngdemo.web.rest;
import com.google.inject.Inject;
import ngdemo.domain.User;
import ngdemo.service.contract.UserService;
import javax.ws.rs.*;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import java.util.List;
@Path("/users")
public class UserRestService {
private final UserService userService;
@Inject
public UserRestService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public List<User> getAllUsersInJSON() {
return userService.getAllUsers();
}
@GET
@Path("{id}")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public User getUserById(@PathParam("id") int id) {
return userService.getById(id);
}
@POST
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public User create(User user) {
return userService.createNewUser(user);
}
@PUT
@Path("{id}")
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public User update(User user) {
return userService.update(user);
}
@DELETE
@Path("{id}")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public void remove(@PathParam("id") int id) {
userService.remove(id);
}
}
You can clone a copy of this project here: https://github.com/draptik/angulardemorestful.
To checkout the correct version for this demo, use the following code:
git clone git@github.com:draptik/angulardemorestful.git
cd angulardemorestful
git checkout -f step4-angularjs-crud
In case you are not using git you can also download the project as ZIP or tar.gz file here: https://github.com/draptik/angulardemorestful/releases/tag/step4-angularjs-crud
